Link-Assistant.com, the Belarus-based developers of SEO PowerSuite software have published a new report entitled Ranking Factors 2020: Facts and Myths.
Below is the meat of Link-Assistant.com's developers' predictions about what ranking factors Google will be using in 2020, as they see them.
In case you're in a hurry, I've highlighted the critical, actionable ones in green.
Domain age and registration length
Neither are ranking factors
Keyword domains
Happening to have keywords in a company's domain name is "kind of unrelated to their current ranking".
Keywords in a page's URL
A keyword in a URL is a ranking factor but "insignificant compared to other ranking factors".
Country Code TLD
Having a country-code TLD (.uk, .fr, etc.) can improve rankings in that country, but maybe at the expense of results elsewhere.
Keyword in <TITLE> tag
Metadata like page titles are among the most important ranking factors, as long as specific to the content of the page.
Keyword in <META Description> tag
Google has not used this as a ranking factor since 2009. Ditto <META keyword> tag.
Keyword in Headline <H1, etc.> tags
Probably a good idea since headline tags help Google understand the context and structure of a page better.
Image optimization
Image ALTs, titles, captions and locations taken together are likely significant ranking factors.
TF-IDF (Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency)
This statistic intended to reflect the importance of a word to the page is an old technique, and Google has a number of newer, better ones.
Content length
Length of a page's content per se is not a ranking factor.
Content comprehensiveness
Google: "Creating compelling and useful content will likely influence your website more than any of the other factors discussed here."
Content recency
Frequent updating probably helps only sites where Google thinks freshness is important, for content like news, trends, politics and events.
Old content
Quality and value of content matter more than age.
Grammar and spelling
Google: "It's always good to fix known issues with a site, but Google's not going to count your typos."
Number of keywords for which a page ranks
Number of ranking keywords per se is unlikely to be a ranking factor. But Google's Query Augmentation Patent seems to suggest that if a page is the best fit for a specific query, it may also rank well for related queries.
Expertise - Authoritativeness - Trust
This comes from Google's Quality Raters Guidelines so isn't used directly as a rating factor.
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords in content
LSI is an old, pre-Internet technique since replaced by newer and better ones, and unlikely to have any impact on rankings.
Internal linking
Internal links and anchor text are important as relevance signals.
User-friendly layout
Sites without much relevant content above the fold may not rank as highly.
Page category
Google's algorithms use a category relevance score that may affect rankings.
Site architecture
How many clicks are required to reach content - and not the URL structure - is what matters to Google.
Valid HTML
Not likely a factor in how Google crawls and indexes your site.
Structured data markup (e.g., schema.org)
May help ranking indirectly by making it easier for Google to understand your content.
HTTPS
Not a critically important factor, but can give you a ranking edge in a competitive market.
Server location
Having your site hosted in your target country is likely to improve rankings in that country.
Page speed
Google has used page speed as a ranking factor for mobile search since July 2018.
Mobile usability
Google: "We will be expanding our use of mobile-friendliness as a ranking signal. This change will affect mobile searches in all languages worldwide and will have a significant impact in our search results."
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
Not a direct ranking signal but may improve site quality as perceived by Google.
Clickthrough rate (CTR), bounce rate, dwell time
Not used as ranking factors but a good conversion rate couldn't hurt.
Pogo-sticking
Google considers moving back and forth between different search returns is normal user behavior, and unlikely to be used as a ranking factor anytime soon.
Direct traffic:
Google denies any connection between traffic to a website and search rankings.
User reviews
Google has a patent that suggests it may use reviews as a ranking factor at some future time, but not now.
======================================
Go here for more on Maine search engine optimization.

 - David
- David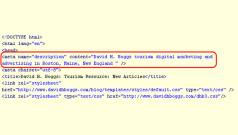




Comments on Google search ranking factors for 2020: another take [PART 1]